Optimizing Smart Home Energy Consumption Strategies
Optimizing Energy Consumption in Smart Homes A Breakthrough in Load Scheduling
Foundation
In an era of rising fuel prices and growing environmental concerns, optimizing energy consumption in households has become more critical than ever. A recent research paper titled “Optimizing Energy Consumption in Smart Homes: Load Scheduling Approaches” by A. I. Ikram and colleagues presents an innovative solution to this challenge. The study explores how smart home energy management systems (SHEMS) can reduce electricity costs and minimize peak-to-average energy consumption ratios while maintaining user comfort.
Challenges
Traditional energy grids rely heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to carbon emissions and environmental degradation. With the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources (RES) like solar panels, managing energy consumption efficiently has become complex. The study addresses this by focusing on:
- Reducing electricity costs for homeowners.
- Balancing energy demand to avoid peak-hour overloads.
- Integrating renewable energy sources like solar power with battery storage.
Proposed Solution
The researchers developed a smart home model equipped with:
- Rooftop solar panels for renewable energy generation.
- Battery storage to store excess solar energy.
- Shiftable and non-shiftable loads to categorize household appliances based on their flexibility in usage time.
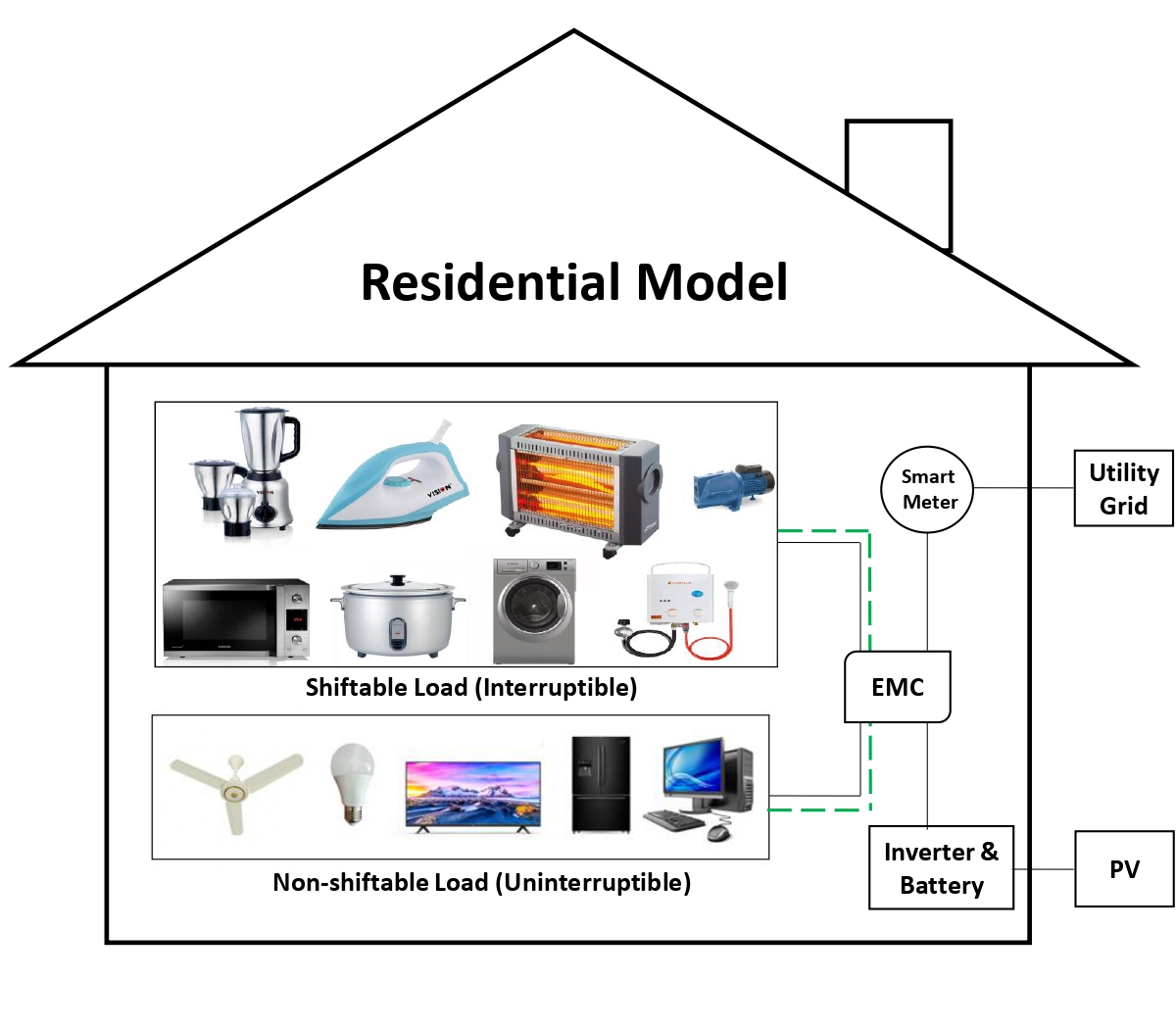
Key Components:
Solar Panel Modeling
- The study used mathematical models to estimate solar energy generation based on sunlight availability.
- Equations accounted for solar radiation, temperature, and panel efficiency to predict hourly energy output.
Battery Storage System
- Excess solar energy was stored in batteries for use during non-generating hours (e.g., nighttime).
- The state of charge (SOC) of the battery was monitored to ensure optimal energy usage.
Load Classification
- Shiftable Loads: Appliances like washing machines, water heaters, and microwaves, whose usage times can be adjusted.
- Non-Shiftable Loads: Essential appliances like refrigerators and lights that must operate continuously.
Optimization Techniques
The study employed two meta-heuristic algorithms to schedule shiftable loads efficiently:
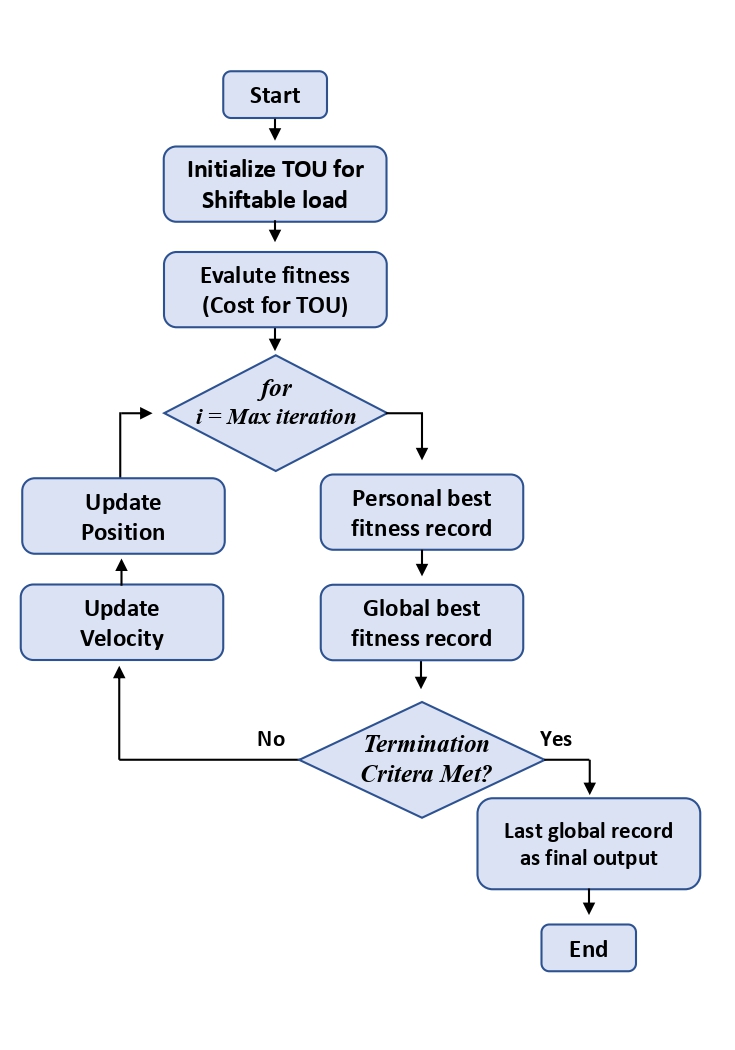
Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
- Inspired by the social behavior of birds, PSO iteratively adjusts the time of use (TOU) for appliances to minimize costs.
- It quickly converges to optimal solutions by balancing individual and collective best positions.
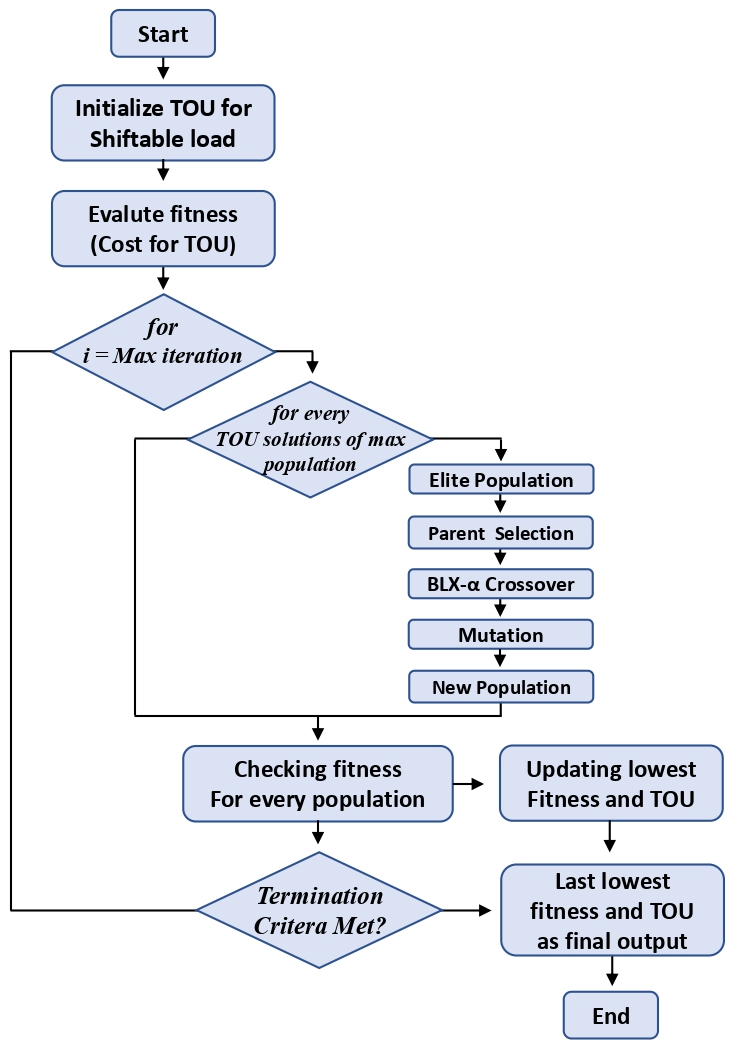
Real-Coded Genetic Algorithm (RCGA)
- A variation of genetic algorithms using real-valued vectors to represent appliance schedules.
- It uses crossover and mutation to explore optimal TOU configurations, ensuring diversity in solutions.
Results and Outcomes
The optimization strategies yielded impressive results:
- Reduced Electricity Costs: Daily costs dropped from 507.12 BDT (before optimization) to 484.33 BDT, a 4.5% reduction.
- Lower Peak Demand: Load curves showed a more balanced energy distribution, avoiding spikes during peak hours.
- User Comfort Maintained: Appliances operated at optimal times without disrupting daily routines.
Key Findings:
- PSO vs. RCGA: Both algorithms achieved similar cost reductions, but RCGA produced a more symmetrical load curve, avoiding excessive peak demands.
- Seasonal Variations: The model was tested for both summer and winter, showing consistent performance across different energy consumption patterns.
Future Directions
The study opens doors for further advancements:
- Hybrid Energy Systems: Integrating wind turbines or diesel generators alongside solar panels.
- Real-Time Pricing Models: Adapting to dynamic electricity tariffs for even greater savings.
- vAdvanced Algorithms: Exploring other optimization techniques like deep reinforcement learning for smarter scheduling.
Conclusion
This research demonstrates how smart home energy management systems can significantly cut costs and improve efficiency. By leveraging renewable energy and intelligent load scheduling, households can contribute to a greener future while enjoying economic benefits.
For homeowners, utilities, and policymakers, these findings highlight the potential of SHEMS in revolutionizing energy consumption. As technology evolves, smarter and more adaptive systems will further enhance these benefits, paving the way for sustainable living.
Interested in the full paper? Check out the original research here (link to the paper).